🏢 📟 🗼 🛠 Introduction
Smart Grids and Energy Management
A smart power grid is an advanced electricity network that optimizes energy distribution using digital technology, automation, and real-time data. It enables bi-directional energy flow, integrates renewable energy sources, and enhances grid stability through automated load balancing and response to energy demand.
Energy management in buildings focuses on monitoring, controlling, and optimizing energy consumption. Smart buildings, residential areas and industrial areas use energy management devices that read metering and measurement devices and control power consumers within the building, thereby reducing costs.
Smart buildings and areas interact with smart grids by feeding excess renewable energy into the grid and adjusting energy usage based on pricing or demand. Microgrids and decentralized energy systems further enhance energy resilience and self-sufficiency.
The benefits are: Lower costs, reduced carbon footprint, increased reliability, and more consumer control.
Fig. 1 illustrates an example of a Smart Grid environment:
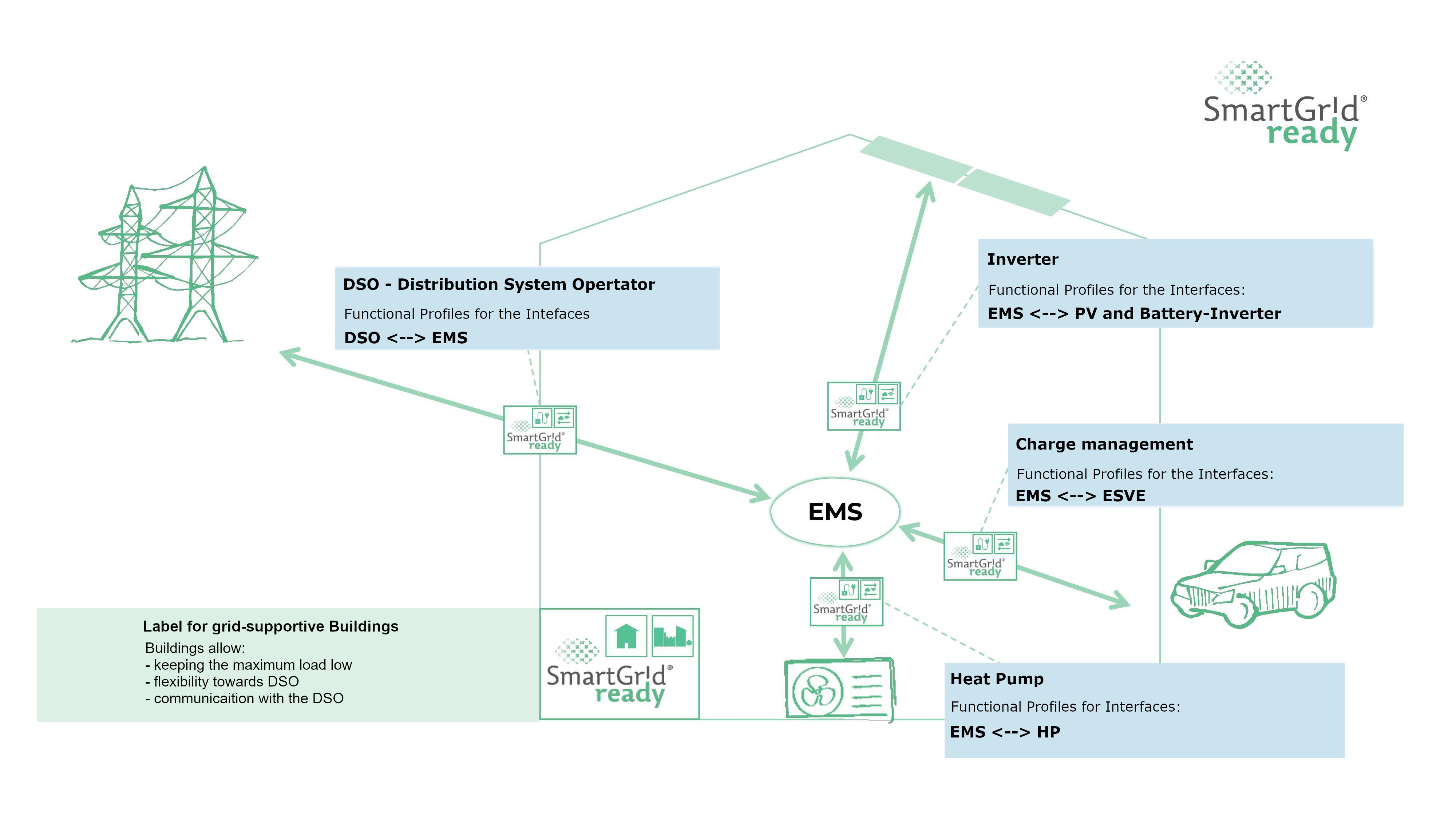
Fig. 1 SmartGridready Environment
Component Name |
Description |
|---|---|
An energy management system for buildings, facilities, or residential areas that optimizes energy consumption by efficiently managing power consumers. |
|
DSO-Interface` |
Interface to the Distribution System (power-grid) Operator. The interface allows load management by the operator and getting tariff information from the DSO. |
Inverter (PV-Inverter) |
Converts the DC electricity generated by PV solar panels into AC electricity, which is used by household appliances and the electrical grid. |
Charge Management (EVSE) |
Infrastructure used to safely deliver electrical power from the grid to an electric vehicle for charging. It includes charging stations, connectors, communication interfaces, and safety mechanisms. |
Heat Pump |
A heat pump is an energy-efficient device that transfers heat rather than generating it directly, providing both heating and cooling for buildings. It works by moving heat between indoor and outdoor environments using a refrigeration cycle. |
SmartGridready Concept
The goal of SmartGridready is to ensure seamless interoperability between energy management devices, energy consuming, energy producing and energy measuring devices, allowing an intelligent power management.
SmartGridready distinguishes between:
Controlled devices referred to as Product
Examples for Product devices are smart-meters, heat pumps, EVSE charging stations, PVA inverters.
Controlling devices referred to as Communicator
Examples for Communicator devices are Energy Management Systems (EMS) and Flexibility Manager devices operated by power grid operators.
SmartGridready establishes a abstract common framework to enable interoperability between system components, allowing Communicator devices to communicate with Product devices in a unified manner, independent of the Product suppliers and their proprietary communication interfaces.
Interoperability is achieved by Functional Profile definitions and External Interface Definition (EID) files in XML that build the core of the SmartGridready specification. The External Interface Definition files define a set of Functional Profiles exposed by a specific Product and the rules to adapt the communication from the generic SmartGridready interface to the proprietary Product interface.
Architecture
Fig. 2 illustrates the basic architecture of a SmartGridready environment.
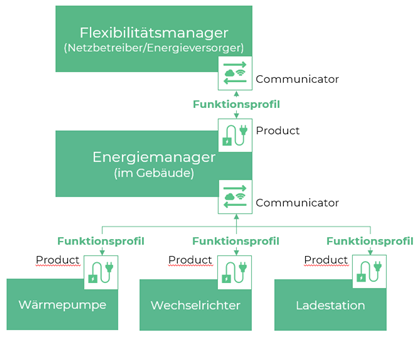
Fig. 2 Basic architecture
Component |
Description |
|---|---|
Acts as a load manager in a power grid. Allows flexible power management by communicating with Energy Managers EMS within sub-networks, residential areas and buildings. |
|
Part of the Flexibility Manager or EMS that communicates with Product devices within the system. SmartGridready allows a communicator communicate with any Product device through standardized interface. |
|
The Functional Profile defines a set of standardized functionalities exposed by a Product device. The Functional Profile forms the core of the SmartGridready standard, enabling flawless communication with any Product device that conforms to the SmartGridready specification. |
|
Acts as a power manager within a building. Provides a Smart Grid Connection Point SGCP receiving commands from Flexibility Manager devices. |
|
Heat pump, PVA inverter, EVSE charging station |
Samples for Product devices |
Further documentation
SmartGridready GitHub projects home